A fast stroll down the drink aisle of any nook retailer reveals the unbelievable ingenuity of meals scientists seeking candy flavors. In some drinks you’ll discover sugar. A weight-reduction plan soda may need a synthetic or pure low-calorie sweetener. And located in almost every little thing else is excessive fructose corn syrup, the king of U.S. sweetness.
I’m a chemist who research compounds present in nature, and I’m additionally a lover of meals. With complicated meals labels claiming meals and drinks to be weight-reduction plan, zero-sugar or with “no synthetic sweeteners,” it may be complicated to know precisely what you might be consuming.
So what are these candy molecules? How can cane sugar and synthetic sweeteners produce such related flavors? First, it’s useful to grasp how style buds work.

Bomin Jeong/EyeEm through Getty Pictures
Style buds and chemistry
The “style map” – the concept that you style completely different flavors on completely different components of your tongue – is much from the reality. Individuals are capable of style all flavors wherever there are style buds. So what’s a style bud?
Style buds are areas in your tongue that include dozens of style receptor cells. These cells can detect the 5 flavors – candy, bitter, salty, bitter and umami. While you eat, meals molecules are dissolved in saliva after which washed throughout the style buds, the place they bind to the completely different style receptor cells. Solely molecules with sure shapes can bind to sure receptors, and this produces the notion of various flavors.
Molecules that style candy bind to particular proteins on the style receptor cells referred to as G-proteins. When a molecule binds these G-proteins, it triggers a sequence of alerts which are despatched to the mind the place it’s interpreted as candy.
NEUROtiker/WikimediaCommons
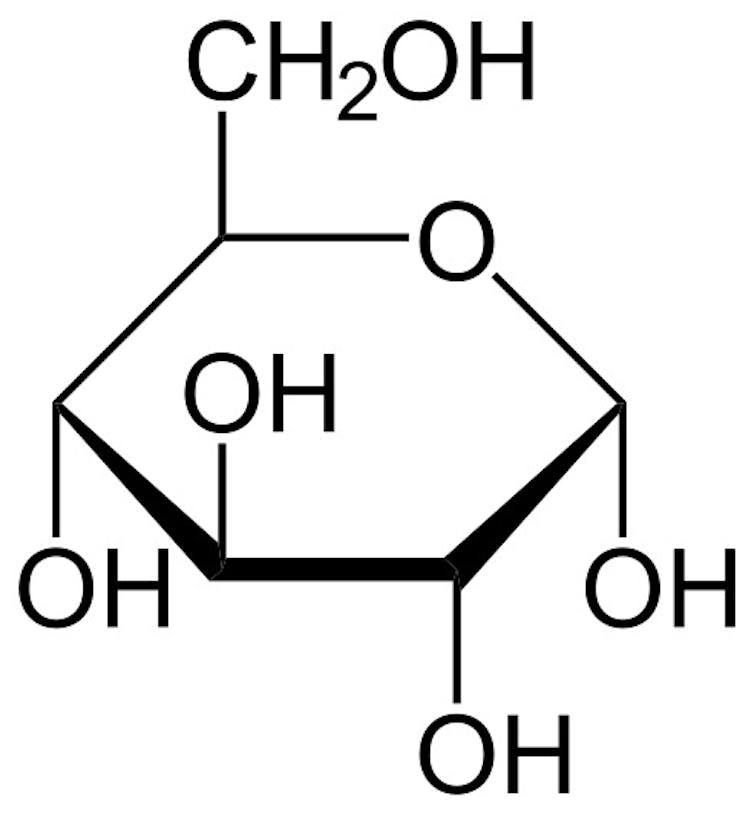
Pure sugars
Pure sugars are varieties of carbohydrates referred to as saccharides which are fabricated from carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. You possibly can think about sugars as rings of carbon atoms with pairs of oxygen and hydrogen connected to the surface of the rings. The oxygen and hydrogen teams are what make sugar sticky to the contact. They behave like Velcro, sticking to the oxygen and hydrogen pairs on different sugar molecules.
The best sugars are single-molecule sugars referred to as monosaccharides. You’ve most likely heard of a few of these. Glucose is probably the most primary sugar and is usually made by vegetation. Fructose is a sugar from fruit. Galactose is a sugar in milk.
Desk sugar – or sucrose, which comes from sugar cane – is an instance of a dissacharide, a compound fabricated from two monosaccharides. Sucrose is shaped when a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule be a part of collectively. Different widespread dissacharides are lactose from milk and maltose, which comes grains.
When these sugars are eaten, the physique processes every of them barely in another way. However ultimately they’re damaged down into molecules that your physique converts into power. The quantity of power from sugar – and all meals – is measured in energy.

Jeff Greenberg/Common Pictures Group through Getty Pictures
Excessive fructose corn syrup
Excessive fructose corn syrup is a staple of U.S. meals, and this hybrid sugar sweetener wants a class all by itself. Excessive fructose corn syrup is made out of corn starch – the principle carbohydrate present in corn. Corn starch is fabricated from 1000’s of glucose molecules bonded collectively. At an industrial scale, the starch is damaged into particular person glucose molecules utilizing enzymes. This glucose is then handled with a second enzyme to transform a few of it into fructose. Usually, excessive fructose corn syrup is roughly 42%-55% fructose.
This mix is nice and low cost to supply however has a excessive calorie content material. As with different pure sugars, an excessive amount of excessive fructose corn syrup is dangerous to your well being. And since most processed meals and drinks are packed stuffed with the stuff, it’s simple to eat an excessive amount of.

Gabriela F. Ruellan/WikimediaCommons
Pure nonsugar sweeteners
The second class of sweeteners might be outlined as pure nonsugar sweeteners. These are meals components corresponding to stevia and monk fruit, in addition to pure sugar alcohols. These molecules aren’t sugars, however they will nonetheless bind to the candy receptors and subsequently style candy.
Stevia is a molecule that comes from the leaves of the Stevia redaudiana plant. It accommodates “candy” molecules which are a lot bigger than most sugars and have three glucose molecules connected to them. These molecules are 30 to 150 instances sweeter than glucose itself. The candy molecules from monk fruit are just like stevia and 250 instances sweeter than glucose.
The human physique has a very onerous time breaking down each stevia and monk fruit. So regardless that they’re each actually candy, you don’t get any energy from consuming them.
Sugar alcohols, like sorbital, for instance, should not as candy as sucrose. They are often present in quite a lot of meals, together with pineapples, mushrooms, carrots and seaweed, and are sometimes added to weight-reduction plan drinks, sugar-free chewing gum and plenty of different meals and drinks. Sugar alcohols are fabricated from chains of carbon atoms as an alternative of circles like regular sugars. Whereas they’re composed of the identical atoms because the sugars, sugar alcohols should not absorbed nicely by the physique so they’re thought of low-calorie sweeteners.

Evan Amos/WikimediaCommons
Synthetic sweeteners
The third option to make one thing candy is so as to add synthetic sweeteners. These chemical compounds are produced in labs and factories and should not present in nature. Like all issues that style candy, they achieve this as a result of they will bind to sure receptors in style buds.
[Over 140,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletters to understand the world. Sign up today.]
To this point, the U.S. Meals and Drug Administration has accredited six synthetic sweeteners. Essentially the most well-known are most likely saccharin, aspartame and sucralose – higher referred to as Splenda. Synthetic sweeteners all have completely different chemical formulation. Some resemble pure sugars whereas others are radically completely different. They’re often many instances sweeter than sugar – saccharin is an unbelievable 200 to 700 instances sweeter than desk sugar – and a few of them are onerous for the physique to interrupt down.
Whereas a candy dessert could also be a easy pleasure for a lot of, the chemistry of how your style buds understand sweetness just isn’t so easy. Solely molecules with the proper mixture of atoms style candy, however our bodies cope with every of those molecules in another way in the case of energy.

This text is a part of a sequence inspecting sugar’s results on human well being and tradition. You possibly can learn the articles on theconversation.com.

